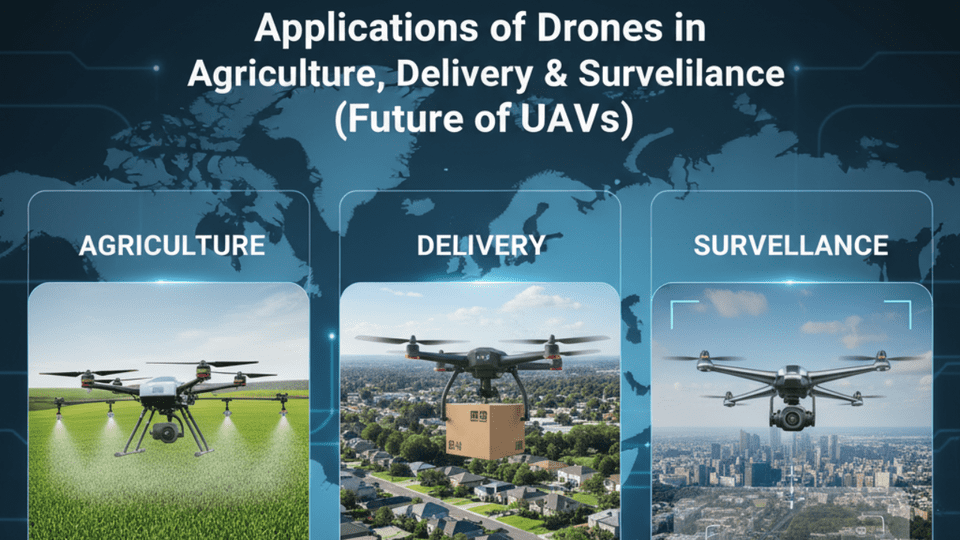
Introduction
Drones are no longer just for aerial photography or weekend hobbyists. They’re transforming entire industries — from farming and logistics to national security.
With advancements in AI, IoT, and autonomous navigation, drones are quickly becoming essential tools of the 21st century.
In this article, you’ll learn about three of the most impactful categories of drone applications:
- Agriculture (Smart Farming)
- Delivery & Logistics
- Surveillance & Security
- Drones in Agriculture (Smart Farming)
How They’re Used
- Crop Monitoring → Multispectral cameras detect crop health (NDVI imaging).
- Pesticide Spraying → Drones with tanks spray precisely, saving resources.
- Planting Seeds → Drones can disperse seeds for reforestation.
- Irrigation Check → Sensors detect water stress in fields.
Benefits
- Increases yield through precision farming.
- Minimizes water & pesticide waste.
- Cuts monitoring costs (no need for planes/helicopters).
- Enables real‑time data collection.
Examples
- DJI Agras Series → crop spraying drones.
- Companies like PrecisionHawk use drones for agriculture analytics.
- Drones in Delivery & Logistics
How They’re Used
- Package Delivery → Drones deliver medical supplies, e‑commerce packages.
- Last‑Mile Delivery → Reduce delivery times in congested cities.
- Emergency Supplies → Deliver to remote/disaster‑struck areas.
Benefits
- Faster delivery (minutes instead of hours).
- Reduced road congestion & carbon emissions.
- Lifesaving: Medicine, blood, vaccines delivered urgently.
Examples
- Amazon Prime Air → testing 30‑min delivery drones.
- Zipline Drones → delivering blood supplies in Africa.
- Google Wing → pilot projects in Australia & US.
- Drones in Surveillance & Security 🛡
How They’re Used
- Border Patrol → Monitor large, difficult terrains.
- Law Enforcement → Crowd monitoring, traffic management.
- Disaster Response → Search & rescue after earthquakes, floods.
- Private Security → Real‑time property monitoring.
Benefits
- Safer — reduces risk to human patrol teams.
- Real‑time bird’s view.
- Can enter dangerous/remote areas quickly.
Examples
- Police departments globally testing surveillance drones.
- Military drones (Predator, Reaper) already core to defense.
- Small commercial drones used by security companies.
Other Notable Drone Applications
- Construction → Site surveys, 3D mapping.
- Filmmaking → Cinematic shots.
- Wildlife Conservation → Anti‑poaching patrols, animal tracking.
- Energy Sector → Inspecting power lines, wind turbines.
Challenges & Concerns
- Privacy → Data misuse & unauthorized surveillance.
- Regulation → Stricter govt rules = slowed adoption.
- Battery Life → Short flight times limit large‑scale missions.
- Safety → Collisions, hacking risks in crowded skies.
Future Trends of Drones in Industry
- Integration with AI & Machine Learning → real‑time decision making.
- Swarm Drones → fleets working together for mapping & disaster relief.
- 5G‑Connected Drones → instant cloud data transfer.
- Drone Taxis → Uber Elevate, Ehang working on passenger drones.
FAQs
Q1: Are agricultural drones affordable for small farmers?
Yes, costs are falling. Renting or drone‑as‑a‑service models are popular.
Q2: Are delivery drones legal today?
Still in testing phase; governments working on air‑traffic regulations.
Q3: Can drones fully replace human security?
No. They’re assistive tools but still need human oversight.
Conclusion
Drones are evolving from gadgets to industry powerhouses:
- Revolutionizing farming with precision agriculture.
- Shortening delivery times with logistics innovations.
- Enhancing surveillance & safety across the globe.
As AI, IoT, 5G, and better batteries merge with drone tech → expect to see flying robots everywhere, from farms and cities to remote jungles and dangerous disaster zones.