Introduction
If Arduino is where you start your electronics journey, ESP boards are where you take your
projects online.
ESP8266 and ESP32 are Wi-Fi and IoT (Internet of Things) microcontroller boards that let you
connect your sensors and projects to a network, control devices from your phone, or send sensor
data to the cloud.
But what’s the difference between ESP8266 and ESP32? Which one should you choose for your
project? Let’s break it down simply.
What is ESP8266?
The ESP8266 is a low-cost Wi-Fi microcontroller launched in 2014 by Espressif. It quickly became
popular with hobbyists because of its:
• Built-in Wi-Fi support.
• Cheap price (~3–3–6 for a NodeMCU/ESP8266 dev board).
• Compatibility with Arduino IDE.
Common ESP8266 Development Boards:
• NodeMCU → beginner friendly, USB support.
• Wemos D1 Mini → tiny board, great for small IoT projects.
Best use cases:
• IoT switches and lights.
• Sending sensor data (temperature, humidity).
• Basic web servers.
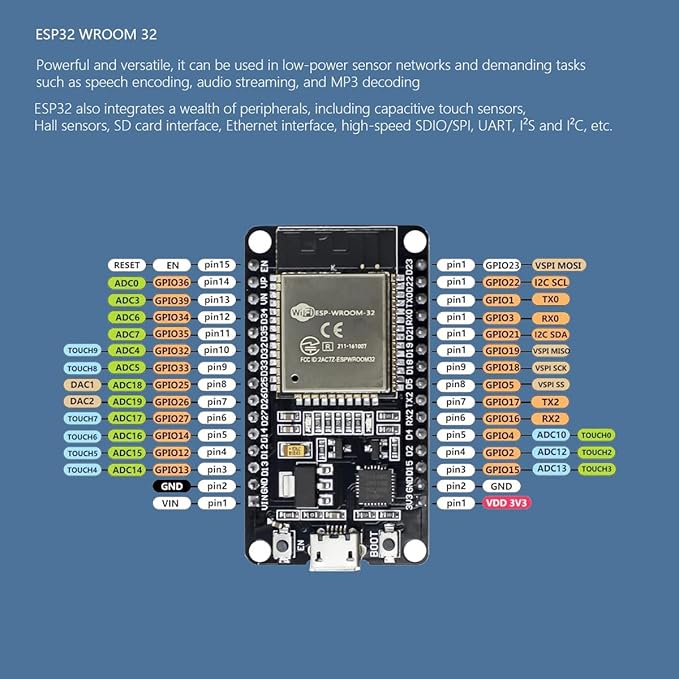
ESP8266 vs ESP32: Key Differences
| Feature | ESP8266 | ESP32 |
| Processor | Single‑core, 80–160MHz | Dual‑core, up to 240MHz |
| RAM | ~160KB | ~520KB |
| Wi‑Fi | Yes | Yes |
| Bluetooth | ❌ No | ✅ Yes (Classic + BLE) |
| GPIO Pins | 11–13 usable | 30+ usable |
| ADC (Analog Inputs) | 1 channel only | 18 channels (12‑bit resolution) |
| Cost | Cheaper (~$5 board) | Slightly higher (~8–8–15 board) |
| Power Efficiency | Medium | High (deep sleep support) |
| Best For | Simple Wi‑Fi IoT devices | Advanced IoT, robotics, AI/ML |
FAQs
Q: Can ESP8266 and ESP32 replace Arduino Uno?
Yes—in most IoT projects with networking, ESP boards are all‑in‑one replacements. But Arduino is still great for pure hardware control/learning basics.
Q: Which one should I learn first?
Start with ESP8266 (NodeMCU) for its simplicity, then move to ESP32 for more advanced projects.
Q: Can ESP8266 or ESP32 run without Wi‑Fi/Internet?
Yes—they’re microcontrollers. Wi‑Fi/Bluetooth is optional depending on your project.
Future Trends & Ecosystem
- ESP8266 remains popular for cheap IoT modules and beginner projects.
- ESP32 is now the standard for advanced IoT/AI edge applications.
- Supported by huge open‑source community — Arduino IDE, MicroPython, PlatformIO.
Conclusion
Both ESP8266 and ESP32 are fantastic boards for stepping into the IoT world:
- ESP8266 → Cheap, small, perfect for simple Wi‑Fi projects.
- ESP32 → Powerful, versatile, with Wi‑Fi + Bluetooth in one chip.
If you’re a beginner, start with ESP8266 (NodeMCU)—your first projects (like Wi‑Fi LED control or sending sensor data online) will be quick wins. Later, upgrade to ESP32 when you want to handle more sensors, communication, or complex IoT automation.